Modern industrial facilities face significant energy challenges due to the extensive use of machinery, heating, cooling, and lighting systems.
Efficient power management has become essential not only for reducing operational costs but also for minimizing environmental impact.
With rising energy costs and global pressure to adopt sustainable practices, industries are looking for practical ways to manage their power consumption effectively.

Understanding Power Consumption in Industrial Facilities
Industrial facilities consume energy in many forms including electricity, thermal energy, compressed air, and fuel-based sources.
Key areas of high energy use include HVAC systems, motors, heavy machinery, and production lines. Monitoring energy consumption can be challenging due to the complexity of industrial operations.
However, understanding where energy is used is the first step in creating effective power management strategies.

Key Principles of Sustainable Power Management
Sustainable power management focuses on using energy more efficiently and integrating renewable sources wherever possible.
Energy efficiency can be achieved by optimizing the operation of equipment and processes to avoid unnecessary consumption.
Integrating renewable sources such as solar or wind helps reduce reliance on conventional power.
Load management is important to balance peak and off-peak usage and avoid wastage.
Continuous monitoring through energy management systems provides real-time insights to make informed decisions.

Energy Audit and Assessment Practices
Regular energy audits are essential for identifying inefficiencies. These audits use tools like smart meters, IoT sensors, and SCADA systems to track energy usage.
Benchmarking consumption against industry standards helps identify areas for improvement. Based on the assessment, facilities can implement practical recommendations to reduce energy usage and improve overall efficiency.

Implementation of Energy-Efficient Technologies
Adopting energy-efficient technologies is crucial for reducing power consumption. High-efficiency motors and drives can significantly lower energy losses in production equipment.
Switching to LED lighting and using smart lighting controls can reduce lighting energy usage.
Variable Frequency Drives allow motors to run at speeds matching the required load, saving energy.
Heat recovery systems capture waste heat and reuse it in the facility.
Advanced HVAC systems ensure effective climate control while using less power.
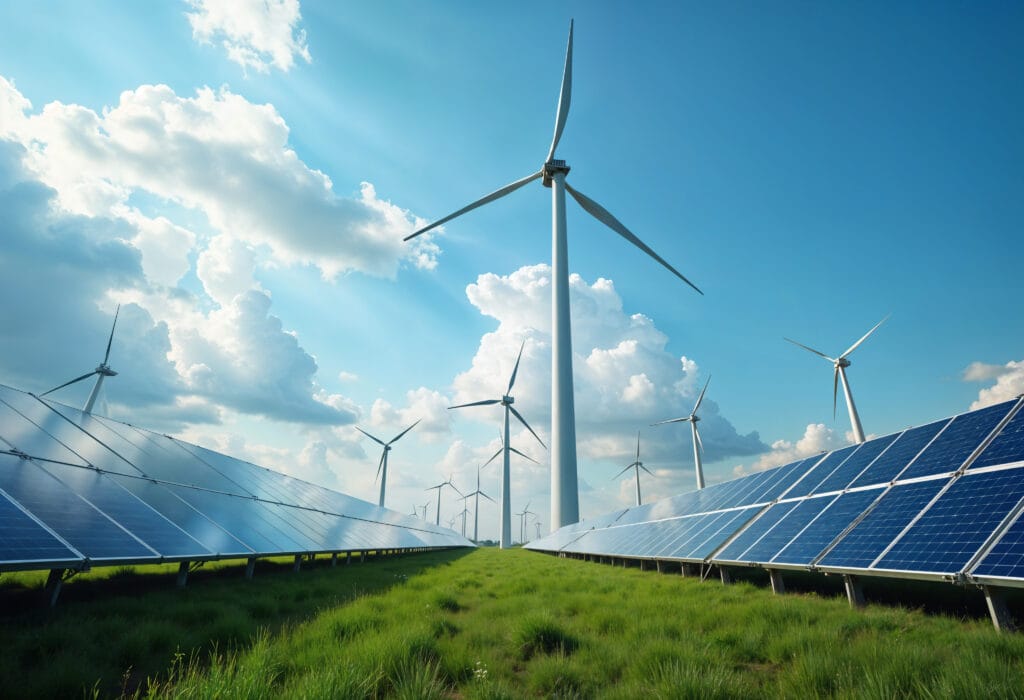
Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources such as solar panels and wind turbines can be installed within industrial facilities to reduce dependence on the grid.
Energy storage systems, including batteries, help balance load and store excess energy for later use.
Hybrid systems that combine grid power and renewable energy provide flexibility and reliability. Governments often provide incentives to encourage renewable energy adoption, making it more accessible for industries.

Smart Power Management Systems
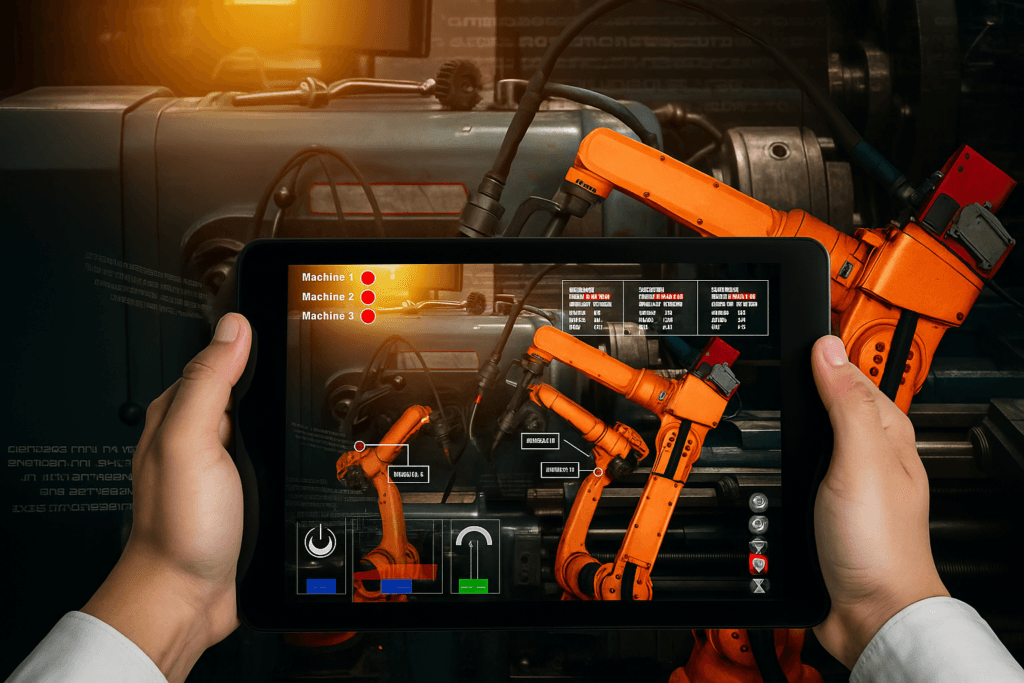
Industrial IoT and automation are reshaping modern power management by enabling smarter and more efficient systems.
Real-time monitoring of energy use provides visibility into consumption and helps in quickly identifying inefficiencies.
Predictive maintenance ensures equipment runs optimally, reducing breakdowns and avoiding unnecessary energy waste.
AI-driven optimization tools analyze usage patterns to manage peak loads, balance supply with demand, and cut energy costs.
Together, these technologies enable intelligent, data-driven energy management that improves efficiency, lowers costs, and supports sustainability.
Conclusion
Sustainable power management in industrial facilities is essential for cost efficiency and environmental responsibility.
A combination of energy audits, energy-efficient technologies, renewable integration, and smart management systems can create significant energy savings.
By adopting these practices, industrial facilities can operate more efficiently while contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable future.











